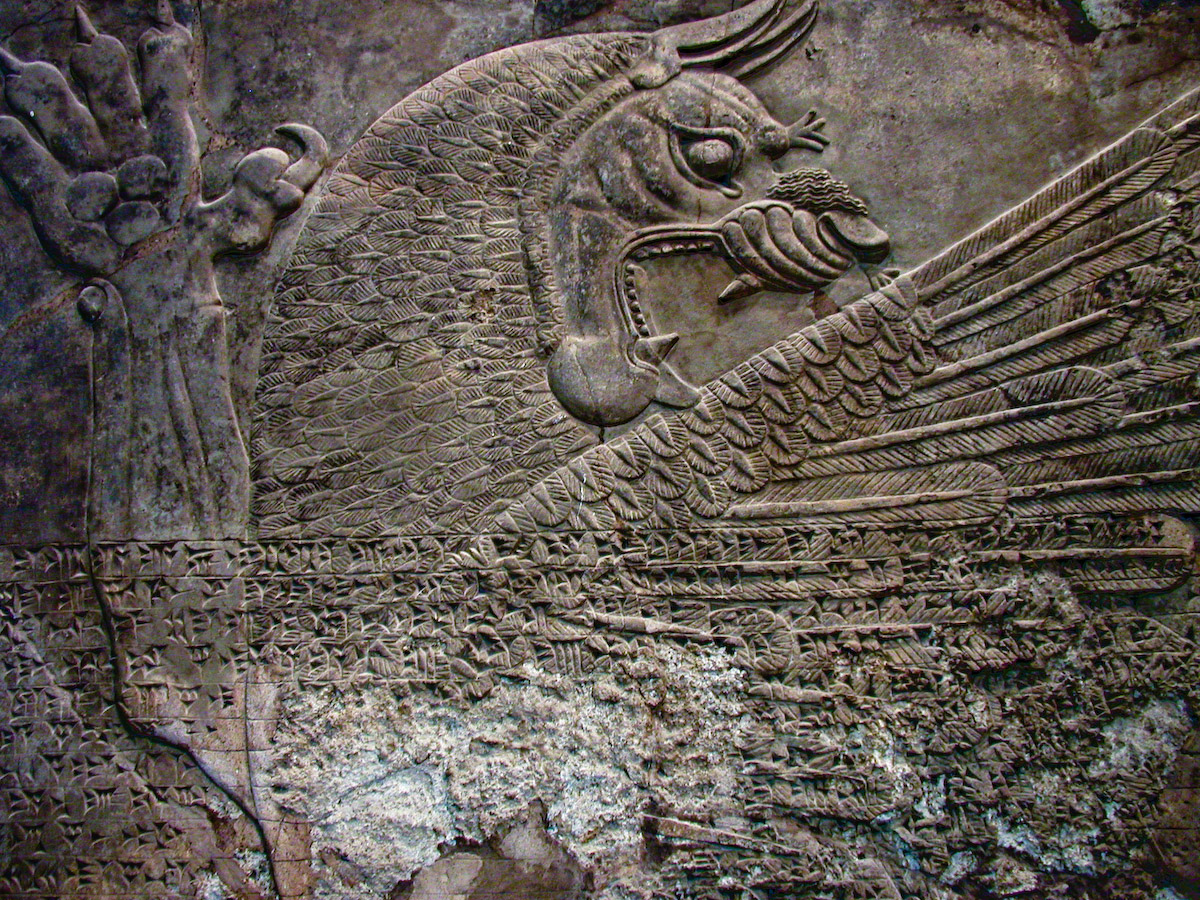
ISIS continues to shock the world with calculated acts of cultural vandalism: taking sledgehammers and electric drills to the millennia-old pieces of art held at Mosul Museum, bulldozing the archaeological sites of Nimrud and Dur-Sharrukin, and most recently releasing a video showing the destruction of artefacts at Hatra. While the predictable images of gleeful vandalism circulate on social media, archaeologists took stock of the antiquities destroyed: statues of the kings of Hatra that form “the finest of all the sculptures unearthed” in the region, several enormous winged bulls with human heads known as lamassu, and assorted irreplaceable relics of the Babylonian, Persian and Roman Empires.
ISIS’s goals are clear: to destroy anything that hints at the region’s pluralistic past, and to strike a blow full of impotent cruelty against the Iraqi government and international organisations such as the UN and UNESCO. Against this backdrop and coupled with the stunning callousness of the group’s ongoing humanitarian atrocities, it has been easy to overlook another loss, one felt particularly acutely by lovers of international literature the world over: that of the still-undeciphered cuneiform tablets caught up in ISIS’s frenzy of destruction. READ MORE…