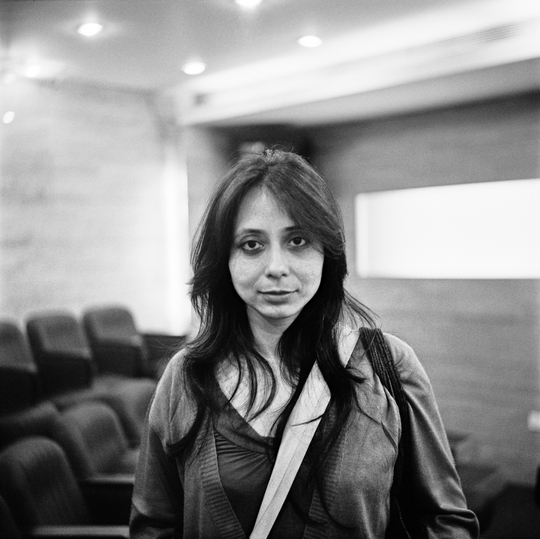
In a conversation about a younger generation of Anglophone writers in India, Annie Zaidi’s name is bound to come up. From poetry to non-fiction to drama to a novella that is both ghost story and romance, her writing continually shifts forms, landscapes, and languages. Zaidi is the editor of Unbound: 2,000 years of Indian Women’s Writing and the author of Gulab, Love Stories # 1 to 14, and Known Turf: Bantering with Bandits and Other True Tales. She is also the co-author of The Good Indian Girl. Her work has appeared in several anthologies including Eat the Sky, Drink the Ocean, Mumbai Noir, Women Changing India, and Griffith Review 49: New Asia Now. Zaidi spoke with me about her influences, process, and literary interests in an email interview.
***
Poorna Swami: Your grandfather was a well-known Urdu writer, and you have said in the past that literature was a big part of your childhood. How has that culture of language and literature influenced your career as a writer? Although you write primarily in English, does Urdu shape your work in any way?
Annie Zaidi: Literature was a big part of my childhood, but not in the sense of literature with a capital L. My family had some literary background, and there were a lot of books around but there were no literary discussions and for many years, I did not have access to a good library. But books were seen as a good thing and we were bought books and comics from an early age. Books were my main source of entertainment and, later, my main solace. I read almost all the time and that turned me into somebody who didn’t know much except the world of words and stories. Turning to literature as a vocation was a very short step from there. READ MORE…