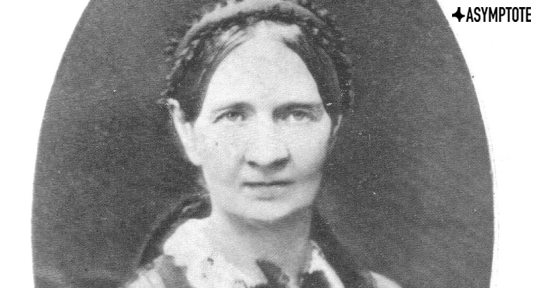On the bicentenary of her birth, Polish writer Narcyza Żmichowska is more relevant than ever. Though only one of her novels has been translated into English, her poetry, letters, and prose influenced feminist thinkers for generations after her death. Read on to learn about Żmichowska’s portrayals of same-sex relationships and her forward-thinking views on womanhood and religion.
Narcyza Żmichowska (1819-1876), author of novels, other prose including educational tracts, poetry, and a vast lifelong correspondence, is regarded by feminists and literary historians as the first Polish woman writer to focus on women’s experiences and issues that particularly affected women’s lives. Often referred to as a “proto-feminist,” she was in fact a feminist by any standard, that is, someone who analysed discrimination against women on grounds of their gender and fought against it, in her case with the pen. She was not a “suffragette” fighting for political rights. The political context of the nineteenth-century Polish lands, divided since 1795 between three partitioning empires, where Polish men also had no political rights, is crucial to understanding the emphasis of her struggle; free-thinking women of her generation were confronted not only by a conservative, predominantly Catholic society with its ideologically entrenched ideals of womanhood, but also by political censorship that suppressed any mention of Polish political independence. That said, many of the issues Narcyza Żmichowska addressed were, in broad terms, similar to those addressed by women across Europe. Well-read in French but also other literatures in French translation and abreast of major developments in European science, including Darwinism, Żmichowska was a European writer par excellence, a fact generally unappreciated thanks to the relative obscurity of nineteenth-century women writing in Polish and other “periphery” languages, caused by their marginalisation by traditional mainstream literary criticism in their own countries and by the lack of translations.